Bloodborne pathogens are infectious microorganisms present in blood and other bodily fluids that can cause serious diseases in humans. Understanding these pathogens is crucial, especially for those in healthcare, emergency response, or any role where exposure to blood or bodily fluids is inevitable. This article provides essential information about bloodborne pathogens, including common types, transmission risks, safety practices, and proper training and protection.
Understanding Bloodborne Pathogens

Bloodborne pathogens are microscopic organisms capable of causing disease. They are commonly found in human blood and other bodily fluids. The pathogens can enter the body through various means, leading to infections and potential long-term health complications. Awareness of these pathogens is vital as they are not visible to the naked eye, making transmission risks challenging to identify without proper precautions.
Training and Awareness Programs for Bloodborne Pathogens
For those in high-risk professions, such as healthcare and emergency services, training on bloodborne pathogens is often required by regulatory agencies like the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). Training programs educate individuals on identifying bloodborne hazards, using PPE effectively, and performing safe cleanup procedures to handle biohazards. Training programs also cover what to do during accidental exposure, such as immediate wound cleaning and seeking medical evaluation. Proper documentation of exposure incidents is crucial, both for the safety of the individual and to meet regulatory standards. Knowing the steps following exposure can be life-saving and helps prevent the spread of bloodborne infections.
The Importance of Immediate Response and Medical Evaluation
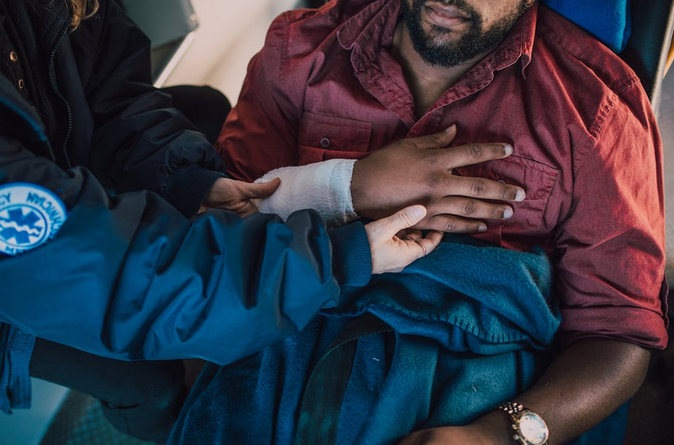
If accidental exposure to bloodborne pathogens occurs, immediate action is necessary. For example, if the exposure involves a cut, the affected area should be washed thoroughly with soap and water. In cases of mucous membrane exposure, flushing the area with water for several minutes is advised. Immediate medical evaluation and post-exposure protocols are essential, particularly if there’s a potential exposure to pathogens like HIV or hepatitis viruses. Post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) may sometimes be recommended, which involves taking antiretroviral medications within hours of exposure to prevent infection. Follow-up medical evaluations can ensure no infection, providing peace of mind and early intervention if necessary.
Bloodborne pathogens are a serious health concern, especially for individuals working in high-risk environments. Understanding the risks, practicing proper safety measures, and receiving adequate training are essential to preventing exposure to these dangerous microorganisms. Individuals can significantly lessen their risk of infection by using protective equipment, safe handling protocols, and quick response to accidental exposure. Prioritizing these preventive steps ensures that people working with or around bloodborne pathogens stay protected while maintaining a safe environment for themselves and others.…
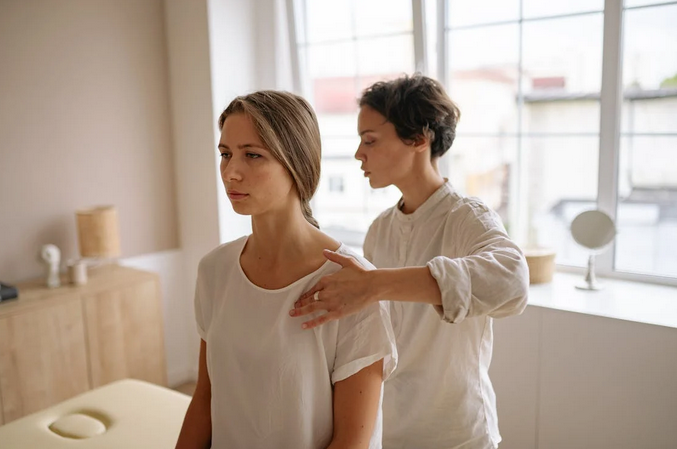

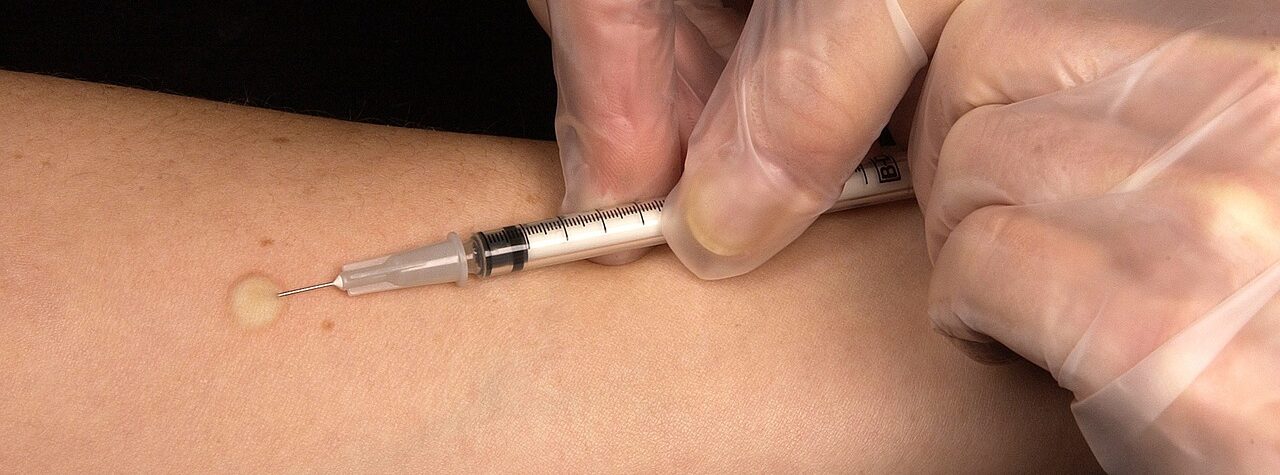









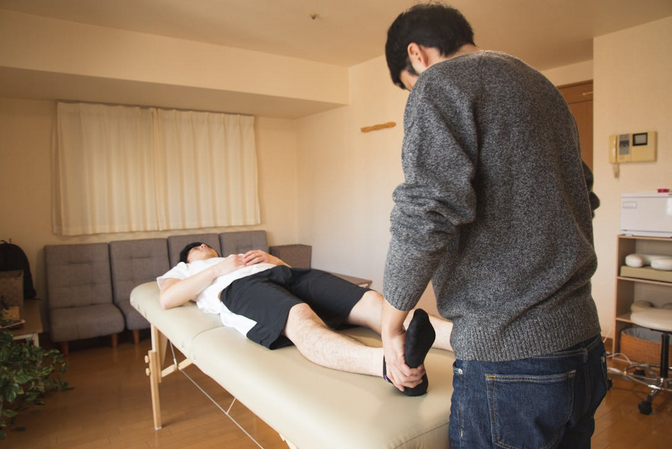




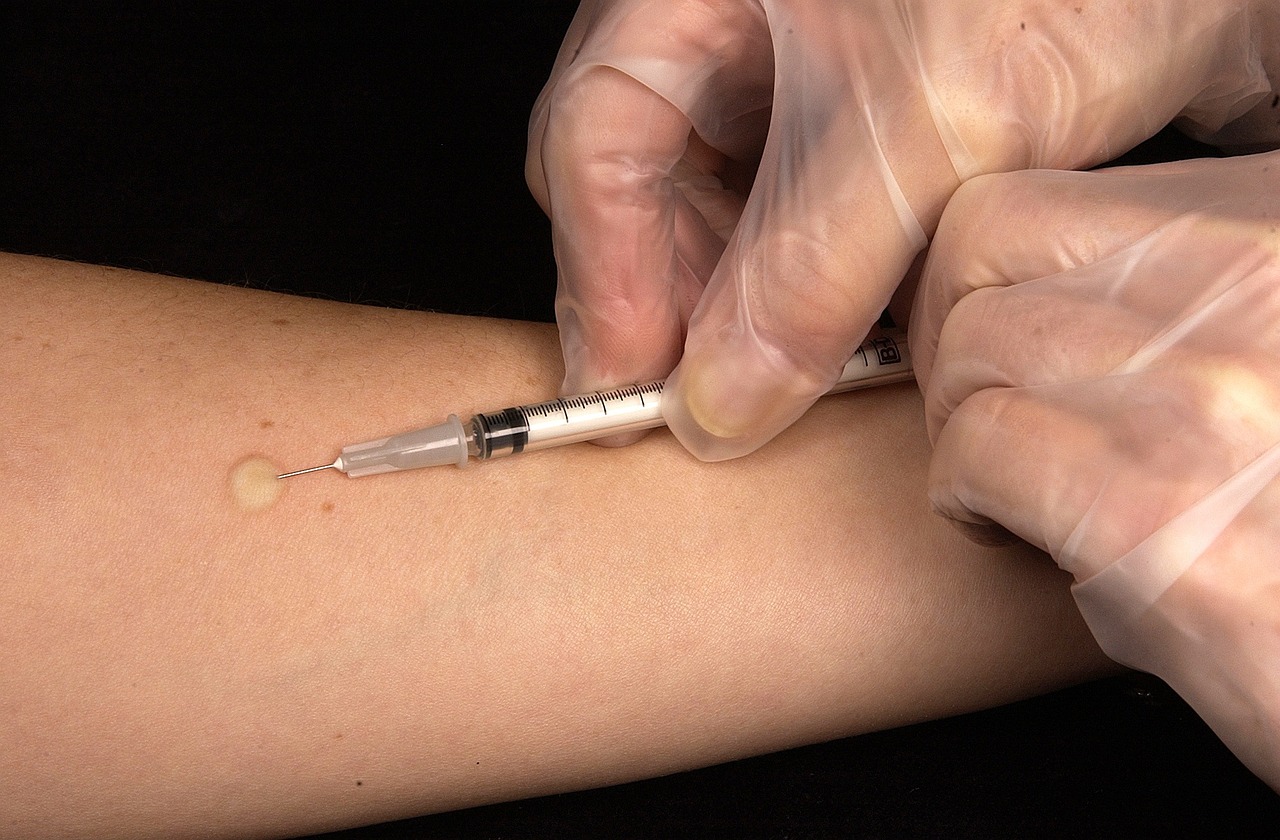
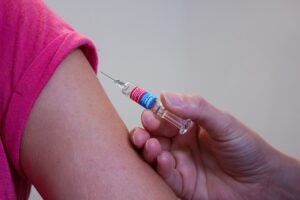 The first health benefit of targeted therapeutic injections is that they can help relieve pain. These injections can significantly reduce inflammation and discomfort by delivering a combination of medications directly to the site of injury or illness. This relief is often almost immediate, allowing people to return to their normal activities more quickly than with other treatments. Many people who have done targeted regenerative injections report that it significantly reduces their pain. In fact, some report feeling almost immediate relief.
The first health benefit of targeted therapeutic injections is that they can help relieve pain. These injections can significantly reduce inflammation and discomfort by delivering a combination of medications directly to the site of injury or illness. This relief is often almost immediate, allowing people to return to their normal activities more quickly than with other treatments. Many people who have done targeted regenerative injections report that it significantly reduces their pain. In fact, some report feeling almost immediate relief.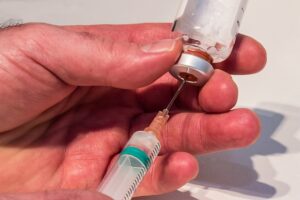 The third health benefit of targeted therapeutic injections is that they can improve joint function. These injections are often used to treat osteoarthritis, a condition that affects the cartilage between bones in the joints. By delivering medications directly to the site of injury or illness, these injections can help reduce inflammation and improve joint function. This can help people increase their range of motion and reduce the risk of further injury. Many people are known to suffer from joint pain, so this type of therapy may be a great option for them.
The third health benefit of targeted therapeutic injections is that they can improve joint function. These injections are often used to treat osteoarthritis, a condition that affects the cartilage between bones in the joints. By delivering medications directly to the site of injury or illness, these injections can help reduce inflammation and improve joint function. This can help people increase their range of motion and reduce the risk of further injury. Many people are known to suffer from joint pain, so this type of therapy may be a great option for them.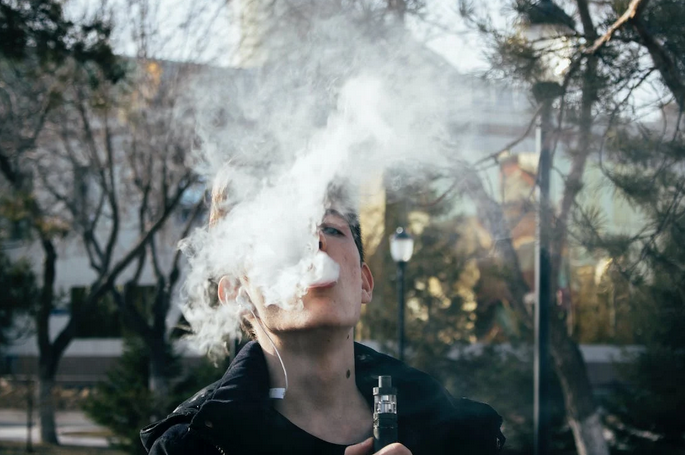
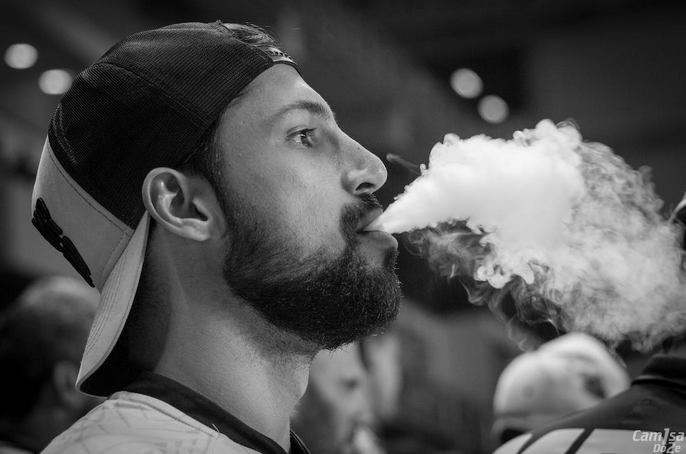 The first advantage why vaping is better over smoking is that it’s much less addictive. While smoking cigarettes can be highly addictive as the nicotine in them acts on the brain’s reward system, e-cigarettes contain far less nicotine than traditional cigarettes, making them much less habit-forming. Many people think that vaping is as addictive as smoking, but studies have shown that this isn’t the case. In fact, medical professionals advise people to consider vaping as an alternative to smoking if they want to quit. This way, they can gradually reduce their nicotine intake until they are free from smoking.
The first advantage why vaping is better over smoking is that it’s much less addictive. While smoking cigarettes can be highly addictive as the nicotine in them acts on the brain’s reward system, e-cigarettes contain far less nicotine than traditional cigarettes, making them much less habit-forming. Many people think that vaping is as addictive as smoking, but studies have shown that this isn’t the case. In fact, medical professionals advise people to consider vaping as an alternative to smoking if they want to quit. This way, they can gradually reduce their nicotine intake until they are free from smoking. The second advantage why vaping is better over smoking is that it actually has fewer toxins. Cigarette smoke contains over 7,000 chemicals and compounds, including many known carcinogens. On the other hand, the vapor produced by an electronic cigarette contains fewer than 5 ingredients, none of which are carcinogenic. This means you reduce exposure to harmful toxins when switching to vaping. Today, many different types of e-cigarettes are available, so you can find one that fits your needs. Depending on your budget, you can choose from disposable, non-disposable, and refillable electronic cigarettes.
The second advantage why vaping is better over smoking is that it actually has fewer toxins. Cigarette smoke contains over 7,000 chemicals and compounds, including many known carcinogens. On the other hand, the vapor produced by an electronic cigarette contains fewer than 5 ingredients, none of which are carcinogenic. This means you reduce exposure to harmful toxins when switching to vaping. Today, many different types of e-cigarettes are available, so you can find one that fits your needs. Depending on your budget, you can choose from disposable, non-disposable, and refillable electronic cigarettes.
 Gummies are one of the most popular ways to take CBD. They are easy to take and offer a discreet way to get your daily dose of CBD. Gummies also come in various flavors, so you can find one that suits your taste. If you are looking for a more potent option, then tinctures may be right.
Gummies are one of the most popular ways to take CBD. They are easy to take and offer a discreet way to get your daily dose of CBD. Gummies also come in various flavors, so you can find one that suits your taste. If you are looking for a more potent option, then tinctures may be right. Vaping is th fastest-acting way to take CBD. When you vape CBD, it is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream, providing relief from pain and inflammation. Vaping is also a great option for those who want to take their CBD dose with them on the go. If you are the type of person who likes to smoke, then you can use a vape pen to take your CBD. Vaping is also a great way to get your daily dose of CBD. Many say that it is more effective than taking it orally.
Vaping is th fastest-acting way to take CBD. When you vape CBD, it is quickly absorbed into the bloodstream, providing relief from pain and inflammation. Vaping is also a great option for those who want to take their CBD dose with them on the go. If you are the type of person who likes to smoke, then you can use a vape pen to take your CBD. Vaping is also a great way to get your daily dose of CBD. Many say that it is more effective than taking it orally.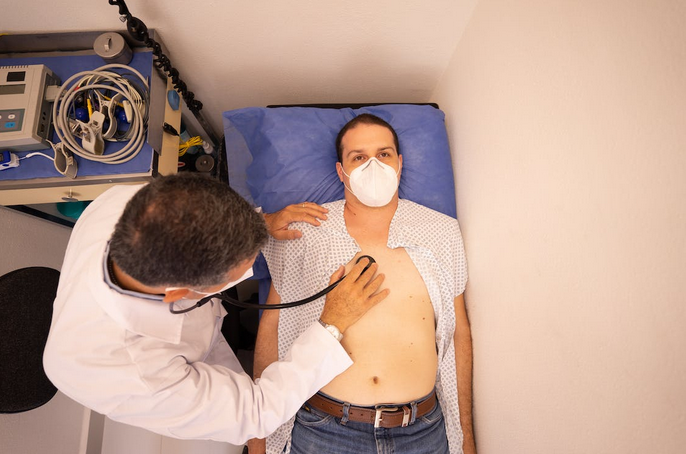
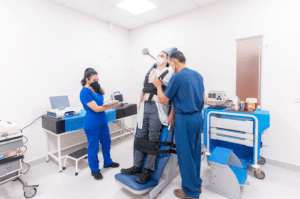 MAT can be an effective treatment for anyone struggling with addiction, but it is especially beneficial for those who have relapsed after trying to quit on their own. The medication helps to reduce the risk of relapse by stabilizing the person’s mood and reducing cravings. MAT is also often used with other treatment methods, such as 12-step programs or inpatient treatment. This allows people to get the best possible care and gives them the best chance of recovery.
MAT can be an effective treatment for anyone struggling with addiction, but it is especially beneficial for those who have relapsed after trying to quit on their own. The medication helps to reduce the risk of relapse by stabilizing the person’s mood and reducing cravings. MAT is also often used with other treatment methods, such as 12-step programs or inpatient treatment. This allows people to get the best possible care and gives them the best chance of recovery.
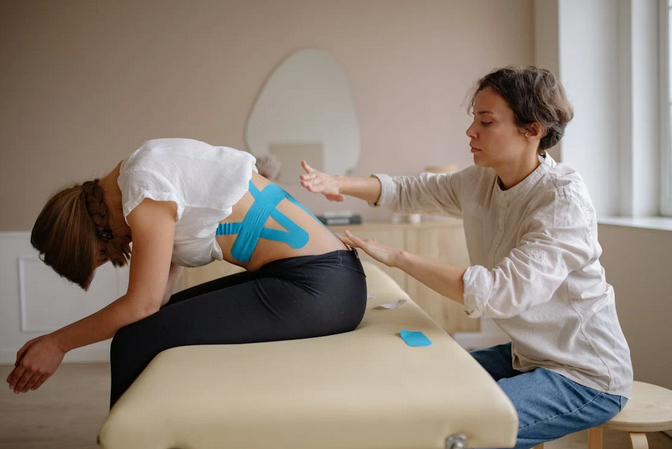
 They will ensure that you’re following the correct technique for each exercise. A physiotherapist can help with proper posture. They can also help you gain strength and flexibility exercises to prevent injury, maintain mobility and independence for as long as possible. If you have a condition requiring physiotherapy, here are some conditions we treat, such as osteoarthritis, back pain, low back pain, shoulder injuries, or cuff injuries.
They will ensure that you’re following the correct technique for each exercise. A physiotherapist can help with proper posture. They can also help you gain strength and flexibility exercises to prevent injury, maintain mobility and independence for as long as possible. If you have a condition requiring physiotherapy, here are some conditions we treat, such as osteoarthritis, back pain, low back pain, shoulder injuries, or cuff injuries. One of the main reasons people seek physiotherapy is to help with aches and pains. A physical therapist can assess your problem areas and develop a treatment regimen that will relieve you of pain, restore motion in your joints, and increase strength and flexibility, so you don’t have any more problems! Another reason people visit a physical therapist is to help them recover from an injury.
One of the main reasons people seek physiotherapy is to help with aches and pains. A physical therapist can assess your problem areas and develop a treatment regimen that will relieve you of pain, restore motion in your joints, and increase strength and flexibility, so you don’t have any more problems! Another reason people visit a physical therapist is to help them recover from an injury.

 Another way to stay healthy during the rainy season is by simply eating healthy foods like vegetables, fruits, and fish. Avoid deep-fried food as these can be harmful to your health, such as dumplings and other Chinese foods like noodles which you might love eating during the year but not when it’s a rainy season because they contain more oil than usual. The rainy season is a time when many of us get sick. It’s not surprising, given how much we’re exposed to colds and flu during this time of year. If you want to stay healthy and avoid the sniffles and more severe illnesses like pneumonia.
Another way to stay healthy during the rainy season is by simply eating healthy foods like vegetables, fruits, and fish. Avoid deep-fried food as these can be harmful to your health, such as dumplings and other Chinese foods like noodles which you might love eating during the year but not when it’s a rainy season because they contain more oil than usual. The rainy season is a time when many of us get sick. It’s not surprising, given how much we’re exposed to colds and flu during this time of year. If you want to stay healthy and avoid the sniffles and more severe illnesses like pneumonia.

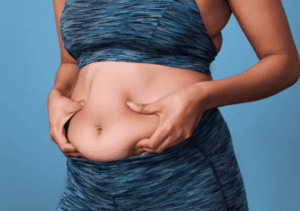




 Selective androgen receptor modulators can be best differentiated by their potency. It is well-known that ligandrol must be the most potent SARM. In contrast,
Selective androgen receptor modulators can be best differentiated by their potency. It is well-known that ligandrol must be the most potent SARM. In contrast,  Andarine is perfect for body recomposition. This means that it is excellent for bulking and cutting. For cutting, you can combine it with Testolone and for bulking, combine it with Ostarine for best results.
Andarine is perfect for body recomposition. This means that it is excellent for bulking and cutting. For cutting, you can combine it with Testolone and for bulking, combine it with Ostarine for best results.
 Stress is a common thing for couples in unhappy relationships. This may affect the state of their mental health and other parts of the body in so many ways. You should completely avoid stress, which is a result of marital conflict. Marriage counseling is the way to go. There are several health benefits you are likely to enjoy if you go for this type of therapy. They include:
Stress is a common thing for couples in unhappy relationships. This may affect the state of their mental health and other parts of the body in so many ways. You should completely avoid stress, which is a result of marital conflict. Marriage counseling is the way to go. There are several health benefits you are likely to enjoy if you go for this type of therapy. They include: stress, which is a leading cause of depression and other mental conditions. This is likely to affect your cognitive function to a certain extent. Going for marriage counseling will help ensure you are on the best terms with your partner. The chances of becoming stressed as a result of marital conflicts are very minimal. You will also be free from conditions such as ulcers.
stress, which is a leading cause of depression and other mental conditions. This is likely to affect your cognitive function to a certain extent. Going for marriage counseling will help ensure you are on the best terms with your partner. The chances of becoming stressed as a result of marital conflicts are very minimal. You will also be free from conditions such as ulcers. your partner is essential for an improved mood. You will have the peace of mind needed, which is also necessary for the excellent state of your health. This is vital in ensuring toxins that accumulate as a result of stress are entirely avoided. How about you go for marriage counseling sessions to enjoy these health benefits.…
your partner is essential for an improved mood. You will have the peace of mind needed, which is also necessary for the excellent state of your health. This is vital in ensuring toxins that accumulate as a result of stress are entirely avoided. How about you go for marriage counseling sessions to enjoy these health benefits.…
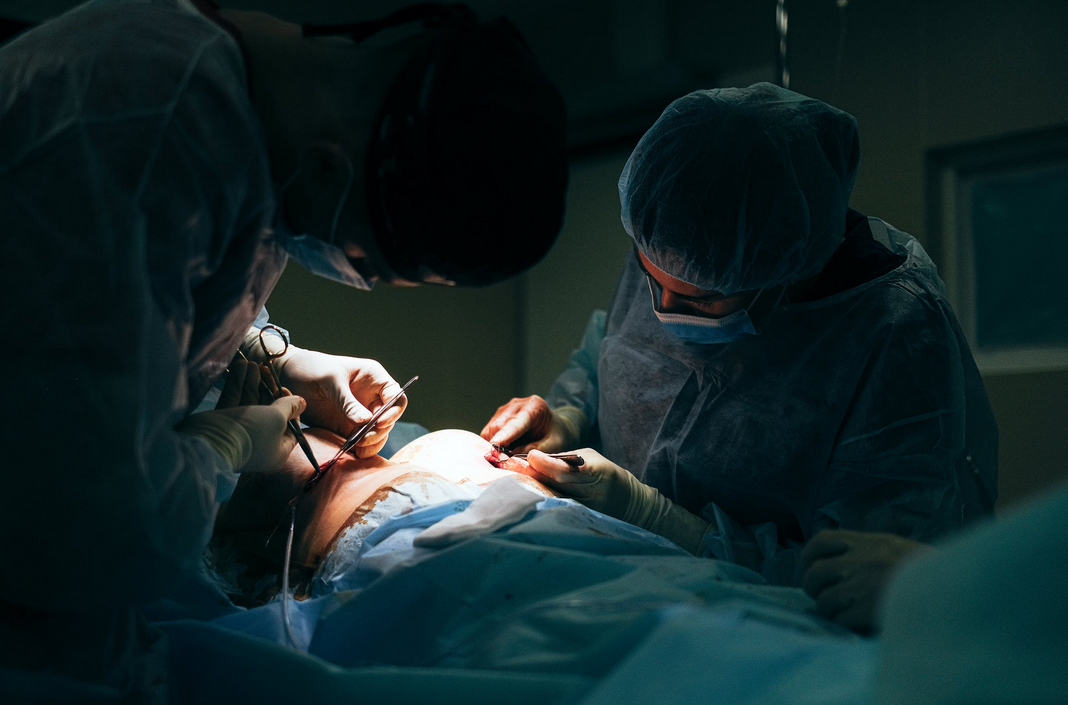 It is essential to make sure that you find a qualified surgeon to operate on you. It is rather unfortunate that many people go to unqualified people to perform some cosmetic surgeries. This is mainly because most skilled cosmetic surgeons tend to charge hefty fees.
It is essential to make sure that you find a qualified surgeon to operate on you. It is rather unfortunate that many people go to unqualified people to perform some cosmetic surgeries. This is mainly because most skilled cosmetic surgeons tend to charge hefty fees.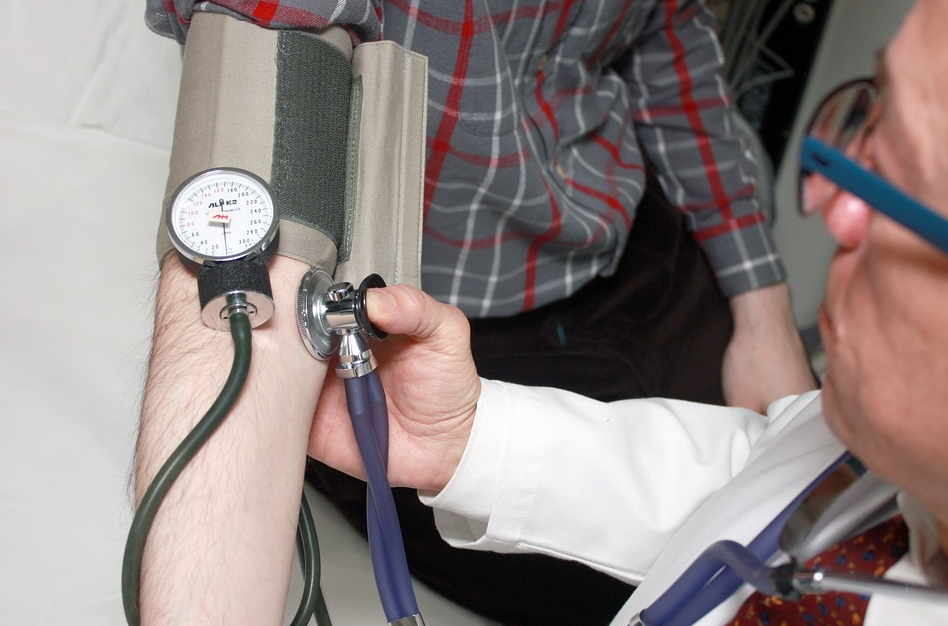 It is essential to make sure that you are in the right health conditions before going for cosmetic surgery. The good news is that most people tend to be in good health when going for the surgery. Make a point of informing the surgeon of all your health records and any health concerns. It is crucial that you be honest and not hide any health condition to ensure the procedure goes smoothly.
It is essential to make sure that you are in the right health conditions before going for cosmetic surgery. The good news is that most people tend to be in good health when going for the surgery. Make a point of informing the surgeon of all your health records and any health concerns. It is crucial that you be honest and not hide any health condition to ensure the procedure goes smoothly. Like any other type of surgery, plastic surgery tends to have risks; you should be prepared if one happens. However, it is essential to note that majority of the risks in plastic are not life-threatening. Most of the risk tends to be the results not coming out as you wanted it. To avoid this, make sure you choose a surgeon with a lot of experience in the field and the required qualifications. Anticipating the recovery time is also crucial. Make sure you ask for the needed time off if you are employed.
Like any other type of surgery, plastic surgery tends to have risks; you should be prepared if one happens. However, it is essential to note that majority of the risks in plastic are not life-threatening. Most of the risk tends to be the results not coming out as you wanted it. To avoid this, make sure you choose a surgeon with a lot of experience in the field and the required qualifications. Anticipating the recovery time is also crucial. Make sure you ask for the needed time off if you are employed.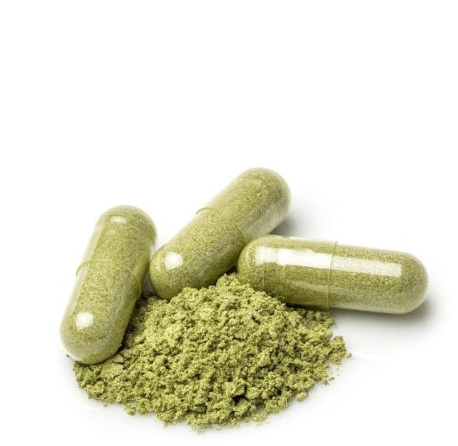
 strains of kratom
strains of kratom 
 Unlike the other products out there, Nutra Organics Collagen Beauty works in amazing ways to make you look healthier and younger from the inside out. It doesn’t have sugar nor carbohydrates. Instead, it has lots of protein, which is essential in revitalizing your body. As long as you use this product on a regular basis, you should be able to see a huge improvement on your skin in no time.
Unlike the other products out there, Nutra Organics Collagen Beauty works in amazing ways to make you look healthier and younger from the inside out. It doesn’t have sugar nor carbohydrates. Instead, it has lots of protein, which is essential in revitalizing your body. As long as you use this product on a regular basis, you should be able to see a huge improvement on your skin in no time.

 Taking care of your health in your forties is more crucial than ever, and it’s time to adjust your routine to your lifestyle. There are many ways to add variety to your workouts to improve posture, strength, bone density, and reduce body fat. At this age, women realize they continuously gain weight. At this point, it is vital to watch their health and be more mindful of their food intake.
Taking care of your health in your forties is more crucial than ever, and it’s time to adjust your routine to your lifestyle. There are many ways to add variety to your workouts to improve posture, strength, bone density, and reduce body fat. At this age, women realize they continuously gain weight. At this point, it is vital to watch their health and be more mindful of their food intake.



 If you are taking up golf for the first time, it is vital to learn how to play golf well. From learning how you can approach the game to understand its importance in club selection, there are several details regarding the game. In fact, if you do not learn from the start, you may find it difficult to play the best golf. Professional golf instructors understand the mechanics of a swing, the need for body positioning and other aspects of the good swing.
If you are taking up golf for the first time, it is vital to learn how to play golf well. From learning how you can approach the game to understand its importance in club selection, there are several details regarding the game. In fact, if you do not learn from the start, you may find it difficult to play the best golf. Professional golf instructors understand the mechanics of a swing, the need for body positioning and other aspects of the good swing.
 There are different ways of how detox can help you lose weight. In fact, if losing weight is your ultimate goal, a detox diet is likely to jumpstart your progress. The good thing about detoxing is that it helps with weight loss management. If you have an ideal weight and want to keep it, then detoxing your body is necessary. You should note that a detox program does not help you immediately, but it sets you on a healthier lifestyle.
There are different ways of how detox can help you lose weight. In fact, if losing weight is your ultimate goal, a detox diet is likely to jumpstart your progress. The good thing about detoxing is that it helps with weight loss management. If you have an ideal weight and want to keep it, then detoxing your body is necessary. You should note that a detox program does not help you immediately, but it sets you on a healthier lifestyle.


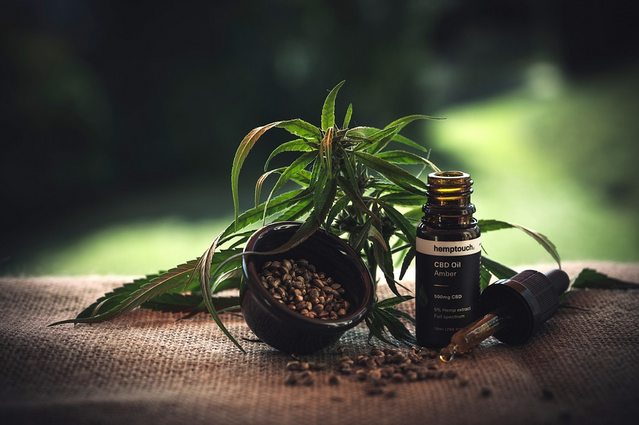
 Properly storing your CBD products not only helps preserve their potency, but also the vital terpenes, cannabinoids, flavonoids, and other elements. It makes CBD oil such a sought-after wellness product. Knowing how to store your CBD oil best ensures you are getting the best results when taking it. The following are the storage measures to observe:
Properly storing your CBD products not only helps preserve their potency, but also the vital terpenes, cannabinoids, flavonoids, and other elements. It makes CBD oil such a sought-after wellness product. Knowing how to store your CBD oil best ensures you are getting the best results when taking it. The following are the storage measures to observe: Similar to direct heat and light, exposure to air can degrade your CBD oil and significantly reduce its effectiveness. Oxygen can alter the chemical balance of CBD oil. Manufacturers take into account the amount of exposure to air and heat when extracting and bottling CBD oil to maximize effectiveness and potency.
Similar to direct heat and light, exposure to air can degrade your CBD oil and significantly reduce its effectiveness. Oxygen can alter the chemical balance of CBD oil. Manufacturers take into account the amount of exposure to air and heat when extracting and bottling CBD oil to maximize effectiveness and potency.
 The thing that makes the red vein kratom stand out from the rest is the alkaloids. It has plenty of alkaloids, and this is what gives it the red color. The alkaloids make the red vein kratom its potent qualities. The potency of the red vein kratom will depend on the number of alkaloids.
The thing that makes the red vein kratom stand out from the rest is the alkaloids. It has plenty of alkaloids, and this is what gives it the red color. The alkaloids make the red vein kratom its potent qualities. The potency of the red vein kratom will depend on the number of alkaloids. Red vein kratom differs in terms of potency. It all depends on the number of alkaloids in the leaves of the kratom. In terms of strength, Bali red kratom is the strongest.
Red vein kratom differs in terms of potency. It all depends on the number of alkaloids in the leaves of the kratom. In terms of strength, Bali red kratom is the strongest.
 You will have to ensure that the rack you consider can fit the type of bike you own. For example, a standard men’s bike will fit easily on any given type of hitch-based rack. Also, women’s bikes and children’s bikes need special adapters, especially with hanging racks available on the market. Also, if you have a racing bike with a carbon fiber frame, you will also need a special adapter to prevent it from being damaged by the rack’s arms.
You will have to ensure that the rack you consider can fit the type of bike you own. For example, a standard men’s bike will fit easily on any given type of hitch-based rack. Also, women’s bikes and children’s bikes need special adapters, especially with hanging racks available on the market. Also, if you have a racing bike with a carbon fiber frame, you will also need a special adapter to prevent it from being damaged by the rack’s arms. You have to check other benefits and features the rack provides. Does it fold up easily so as to access the tailgate or trunk door? Check whether it has large pads that protect the frame of the bike from rub-related wear. What makes your rack apart from other makes and models on the market? It does not matter whether you choose a hanging style, platform, or wheel; each of these options will give you the ability to securely and safely transport your bike. They are great for families that head out for annual vacation.…
You have to check other benefits and features the rack provides. Does it fold up easily so as to access the tailgate or trunk door? Check whether it has large pads that protect the frame of the bike from rub-related wear. What makes your rack apart from other makes and models on the market? It does not matter whether you choose a hanging style, platform, or wheel; each of these options will give you the ability to securely and safely transport your bike. They are great for families that head out for annual vacation.…
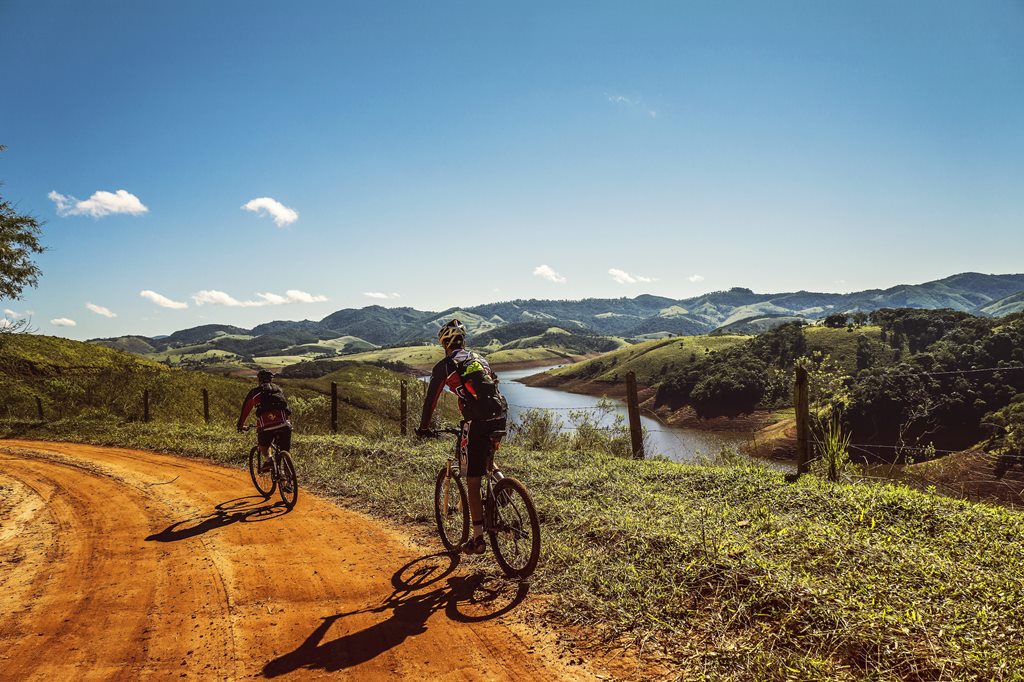

 The weight of a road bike matters when looking for a perfect road bike. Riders should avoid spending their hard-earned money on road bikes that would make the cycling task difficult. The GMC Denali Road bike is designed with the rider’s needs in mind. This model has a lightweight, durable aluminum frame, which makes it an excellent choice for workout activities.
The weight of a road bike matters when looking for a perfect road bike. Riders should avoid spending their hard-earned money on road bikes that would make the cycling task difficult. The GMC Denali Road bike is designed with the rider’s needs in mind. This model has a lightweight, durable aluminum frame, which makes it an excellent choice for workout activities.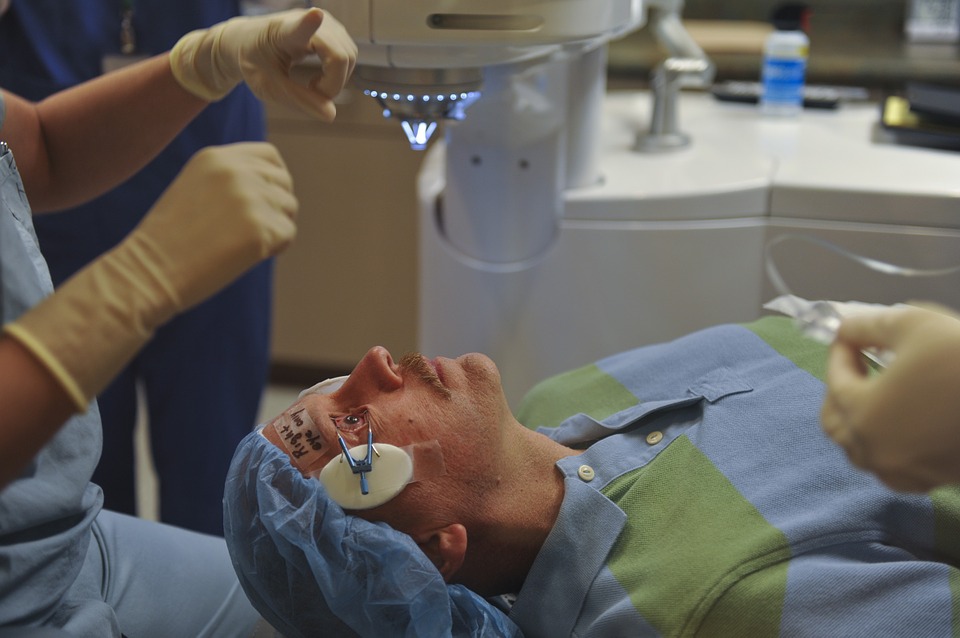
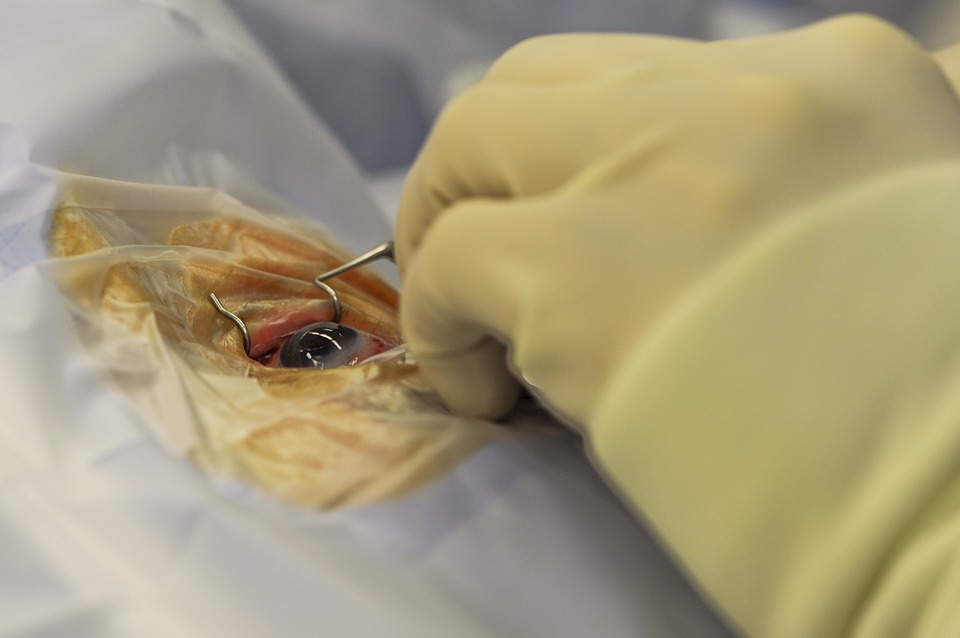 These fillers have hyaluronic acid, which causes binding of water in the skin and as a result, the eyes look plump. Thus, this procedure is more effective for people looking to fill in the hollow areas beneath the eye bags and improving the overall eyes appearance. The effects of the process last for about a year and a half, and it can be used together with Botox.
These fillers have hyaluronic acid, which causes binding of water in the skin and as a result, the eyes look plump. Thus, this procedure is more effective for people looking to fill in the hollow areas beneath the eye bags and improving the overall eyes appearance. The effects of the process last for about a year and a half, and it can be used together with Botox.

 The Ingredients
The Ingredients

 Taking It Is More Natural
Taking It Is More Natural



 Connection with Fond Memories
Connection with Fond Memories Connection with Friends Remains Intact
Connection with Friends Remains Intact
 Rather than allow the water to make its way from your glass straight to your throat, swirl each sip around your mouth using your tongue. Doing this on a regular basis will keep the germs in your mouth from breeding in other places as well.
Rather than allow the water to make its way from your glass straight to your throat, swirl each sip around your mouth using your tongue. Doing this on a regular basis will keep the germs in your mouth from breeding in other places as well.

 Germs are present everywhere, and for this reason, it’s important that you wash your cutting boards, utensils, and hands. Also, you should sanitize all your other cooking utensils. If you want to minimize the chances of food poisoning, you can decide to put on disposable gloves when handling raw food.
Germs are present everywhere, and for this reason, it’s important that you wash your cutting boards, utensils, and hands. Also, you should sanitize all your other cooking utensils. If you want to minimize the chances of food poisoning, you can decide to put on disposable gloves when handling raw food.